Concept
Trước hết, chúng ta cần hiểu DataStore sinh ra với mục đích là gì.
Hiện tại, trong ứng dụng Android, chúng ta có 5 cách để lưu trữ dữ liệu, trong đó SharedPreferences là cách dùng để lưu những dữ liệu đơn giản nhất. Nó chỉ gồm key và value, trong đó value có thể là integer, string…
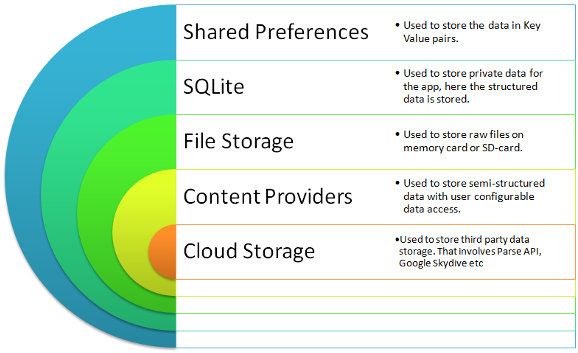
Khi lần đầu mở app, nó sẽ đọc toàn bộ giá trị trong file xml của SharedPrefrences và lưu vào RAM. Quá trình đọc file này lại diễn ra trên UI Thread, nếu chúng ta có rất rất nhiều giá trị khiến cho thời gian thực hiện tác vụ vượt quá 5 giây, nó sẽ gây ra lỗi ANR (Application Not Responding).
Và DataStore được tạo ra chính là để thay thế SharedPreferencs.
DataStore là giải pháp lưu trữ dữ liệu theo dạng cặp key-value hoặc typed objects với protocol buffers.
Tất nhiên, DataStore vẫn chỉ dành để lưu những dữ liệu có cấu trúc đơn giản. Nó sử dụng Coroutines và Flow để lưu data một cách bất đồng bộ và nhất quán.
DataStore gồm 2 loại Preferences DataStore và Proto DataStore, chúng ta cùng nhìn qua bảng so sánh sau:
| Preferences DataStore | Proto DataStore |
|---|---|
| Lưu và truy cập data bằng key | Lưu instance của một loại custom data |
| Không yêu cầu định nghĩa trước loại data | Phải định nghĩa trước loại data bằng protocol buffers |
| Không có type safety | Có type safety |
Preferences DataStore
Create
Để sử dụng Preferences DataStore, chúng ta cần tạo một instance DataStore<Preferences> bằng property delegate với keyword preferencesDataStore.
| |
Read
Trước hết, chúng ta có 7 function tương ứng với 7 loại data:
intPreferencesKey()longPreferencesKey()doublePreferencesKey()floatPreferencesKey()booleanPreferencesKey()stringPreferencesKey()stringSetPreferencesKey()
Khi đọc data, chúng ta cần dùng function tương ứng với giá trị mà chúng ta cần lưu. Ví dụ để lưu một biến counter dạng số nguyên để đếm số lần user mở app, chúng ta có thể dùng cách sau:
| |
Điểm khác biệt với SharedPreferences chính là ở đây, data được trả về dưới dạng Flow. Giờ đây, các layer phía trên như Repository có thể observe data một cách thống nhất, không cần quan tâm nó đến từ DataStore, Room database hay Server, bởi vì tất cả đều được return dưới dạng Flow.
Write
Để ghi dữ liệu, chúng ta dùng function edit, cũng khá giống với SharedPreferences.
| |
Proto DataStore
Trước khi tìm hiểu về Proto DataStore, chúng ta cần dạo qua một vòng về protocol buffers.
Protocol buffers
Đây là một một kiểu định dạng dữ liệu mà không phụ thuộc vào ngôn ngữ lập trình hay platform. Nó giống như JSON nhưng nhỏ và nhanh hơn nhiều lần. Protocol buffers cũng được giới thiệu là định dạng dữ liệu được sử dụng phổ biến nhất tại Google.
- Nó dùng để lưu các dữ liệu nhỏ gọn
- Phân tích cú pháp nhanh
- Hỗ trợ nhiều ngôn ngữ lập trình như C++, C#, Dart, Go, Java, Kotlin, Python
- Tối ưu hoá chức năng thông qua các class được generate tự động
Ví dụ một message về thông tin user gồm tên, id và email:
| |
Để so sánh về hiệu năng so của Protocol buffers so với JSON, chúng ta thử gọi 500 GET requests từ một app Spring Boot này tới app Spring Boot khác với 2 môi trường có nén và không nén data. Và đây là kết quả:
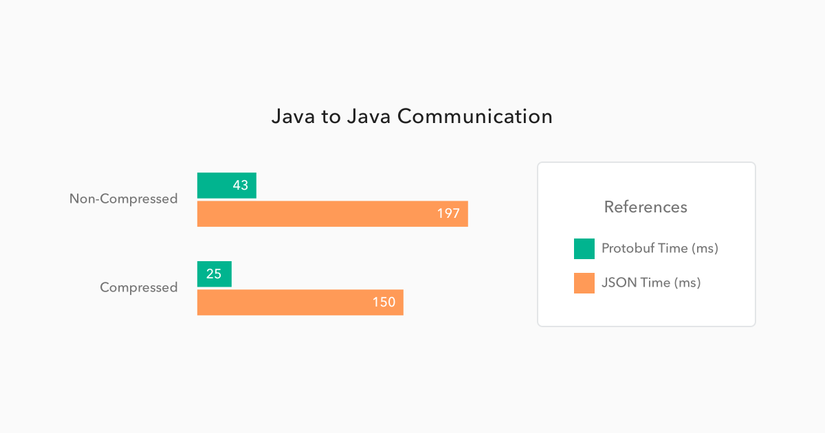
Chúng ta có thể thấy Protocol buffer nhanh hơn từ 5 đến 6 lần so với JSON.
Create
Để sử dụng Proto DataStore, chúng ta phải định nghĩa loại data bằng một file proto settings.pb trong folder app/src/main/proto/ như sau:
| |
Sau đó, tiếp tục khai báo một object implement class Serializer<T> với T là kiểu dữ liệu đã được định nghĩa trong proto file.
| |
Và cuối cùng là sử dụng property delegate với keyword dataStore để tạo một instance của DataStore<T>.
| |
Read
Tương tự như Preferences DataStore, chúng ta cũng dùng DataStore.data để trả về một Flow.
| |
Write
Để ghi data vào Proto DataStore, chúng ta có function updateData().
| |
So sánh với SharedPreferences
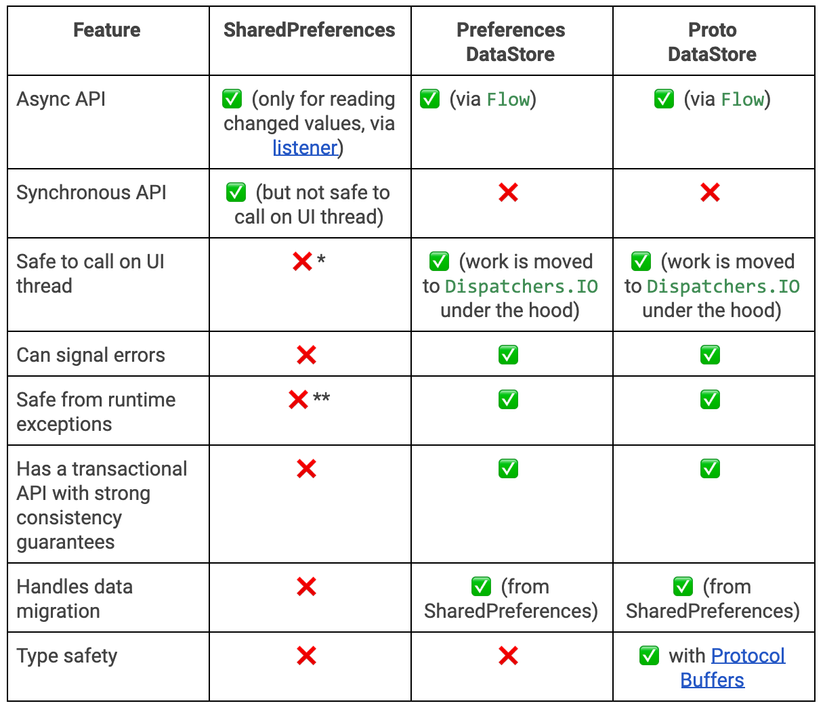
Migrate from SharedPreferences to Preferences DataStore
Để migrate, chúng ta truyền SharedPreferencesMigration vào param produceMigrations. DataStore sẽ tự động migrate cho chúng ta.
| |
Migrate from SharedPreferences to Proto DataStore
Trước tiên, chúng ta cần khai báo UserProfile và UserProfileSerializer tương tự như các bước ở trên. Sau đó viết một mapping function để migrate từ cặp key-value trong SharedPreferences sang loại dữ liệu trong Proto DataStore.
| |
References
- https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/architecture/datastore
- https://protobuf.dev/programming-guides/proto3
- https://android-developers.googleblog.com/2020/09/prefer-storing-data-with-jetpack.html
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9986734/which-android-data-storage-technique-to-use
- https://auth0.com/blog/beating-json-performance-with-protobuf
- https://proandroiddev.com/is-jetpack-datastore-a-replacement-for-sharedpreferences-efe92d02fcb3
- https://kinya.hashnode.dev/migrating-sharedpreferences-to-datastore-ckxzlvda101by8rs1c8bg4wdx
- https://amitshekhar.me/blog/jetpack-datastore-preferences
